Hepatic encephalopathy and traffic accidents
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a frequent complication in patients with chronic liver disease. HE is a complication of cirrhosis that is associated with psychomotor slowing and an increased risk of accidents at…
A nuclear receptor links HIV drugs with liver disease
Before the advent of antiretroviral drugs, the prognosis for patients with AIDS was extremely poor. However, new antiretroviral treatments have revolutionised care for patients with HIV/AIDS, making lifelong viral suppression possible and…
Physical activity linked to reduced risk of liver cancer
Liver cancer is a leading cause of cancer death, with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) accounting for 85–90% of all primary liver cancers. In a recent issue of Journal of Hepatology, Dr Baumeister et…
MICROB-PREDICT – €15 million EU funded microbiome research project kicks off
SCIENTIFIC PRESS RELEASE Developing personalised targets for treatment of decompensated cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) Barcelona, Spain - An EU Horizon 2020-financed project investigating methods to better understand the role of…
New liver failure treatment could be here by 2020
DIGESTIVE WELLNESS 14 December 2018 170,000 people in Europe die from liver failure every year. The cirrhosis death toll could be cut from 2020, thanks to advanced dialysis technology being trialled in…
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease explains chronic-liver-disease-related mortality
Alcoholic liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are the leading etiologies for chronic liver disease chronic-liver-disease-related deaths in the United States over the last decade, according to the results of…
Transforming the landscape of liver disease in the UK
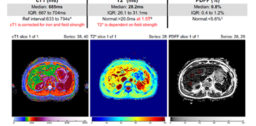
Perspectum Diagnostics released details regarding the latest version of its LiverMultiScan magnetic resonance imaging technology which identified nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, according to a press release. The latest version…