Living donor transplantation offers a safe alternative for liver transplant patients
Living donor liver transplants can reduce waitlist time and deaths according to a new study published in the Journal of Hepatology
Amsterdam, September 26, 2022 – Demand for donor livers for transplant patients outstrips supply with over 15% of waitlist patients dying after a year. A new international study offers support for increasing the use of living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) in Western countries and reducing the imbalance between organ supply and demand. This study is reported in the Journal of Hepatology, the official journal of the European Association for the Study of the Liver, published by Elsevier.
LDLT is when a portion of the liver from a healthy living person is removed and placed into someone whose liver is no longer working properly. The donor’s remaining liver regrows and returns to its normal size, volume, and capacity within a few months after the surgery. Although the waiting period for a deceased donor transplant can be over five years, LDLT remains uncommon compared to deceased donor liver transplantation (DDLT) in Western countries compared to those in Asia.
Identifying differences in outcomes and other transplant characteristics may help identify areas for healthcare improvement and clarify whether expanding LDLT practices can be justified in countries that rely primarily on DDLT.
“There has been a growing interest in strategies to alleviate the increasing demand for transplantation and the unacceptably high mortality on the liver transplant waitlist,” explained Gonzalo Sapisochin, MD, PhD, MSc, Division of General Surgery, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada. “One such approach is LDLT, which can expand the number of grafts available for transplantation. However, short- and long-term outcomes need to be maintained for both the donors and recipients. We therefore sought to compare donor and recipient characteristics and post-transplant outcomes after LDLT.”
This is a retrospective multicenter study of adults aged 18 years or older who underwent primary LDLT between January 2008 and December 2018 as reported by three national liver transplantation registries: United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS; US), National Health Service Blood and Transplantation (NHSBT; UK), and the Canadian Organ Replacement Registry (CORR; Canada). Patients undergoing retransplantation or multi-organ transplantation were excluded. Investigators compared recipient and donor characteristics, temporal trends, and post-LDLT outcomes across the three registries. In addition, they sought to evaluate outcomes for LDLT compared with DDLT within each of the countries.
A total of 2,954 LDLTs were performed in these countries, 2,328 of which took place in the US, 529 in Canada, and 97 in the UK. Canada performed the highest proportion of LDLT procedures over time. Investigators were pleasantly surprised to see that long-term outcomes were excellent despite relatively low use of LDLT in Western countries. The one-, five-, and 10-year patient survival rates were 92.6%, 82.8%, and 70.0% in the USA; 96.1%, 89.9%, and 82.2% in Canada; and 91.4%, 85.4%, and 66.7% in the UK, respectively.
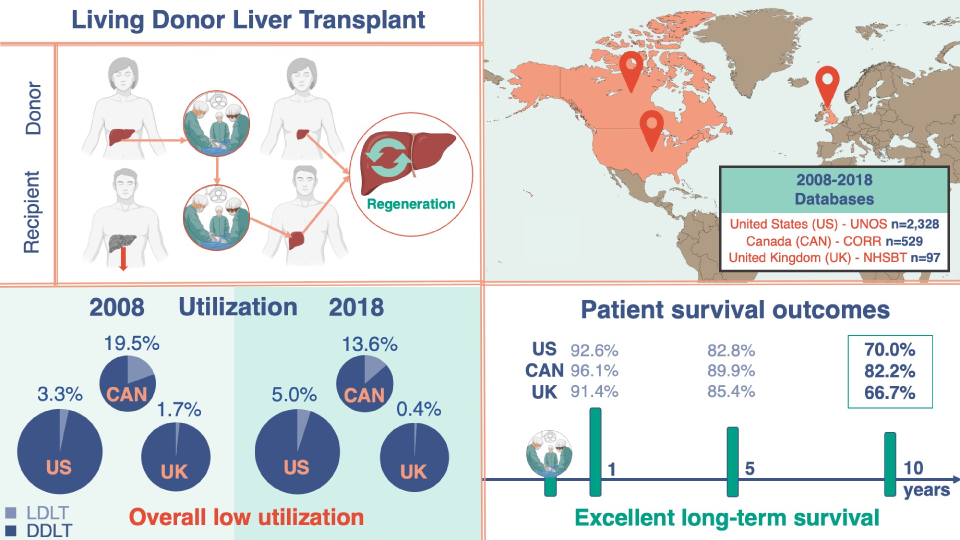
Caption: Living Donor Liver Transplantation (LDLT) in the US, Canada, and UK. Top left: Regeneration of the donor liver in both donor and recipient after transplantation. Top right: Numbers of living donor liver transplants registered in the US, Canada, and UK. Lower left: Overall low use of LDLT compared to DDLT in the US, Canada, and UK. Lower right: One-, five- and 10-year survival outcomes in the US, Canada, and UK after LDLT (Credit: Journal of Hepatology).
This analysis of LDLT demonstrates that despite the low use of LDLT in Western countries compared to Asian countries, long-term survival is excellent. In addition, the mortality risk is not statistically significantly different between these three countries.
“This study offers support for increasing the use of LDLT in Western countries because it provides an opportunity to reduce the imbalance between organ supply and demand and, as a result, offers waitlist candidates the possibility of earlier transplantation and decreased mortality on the transplant waitlist,” commented Dr. Sapisochin
—
Notes for editors
The article is “Low utilization of adult-to-adult LDLT in Western countries despite excellent outcomes: International multicenter analysis of the US, UK, and Canada,” by Tommy Ivanics, MD, MPH, David Wallace, MSc, Marco P.A.W. Claasen, MD, Madhukar S. Patel, MD, MBA, ScM, Rushin Brahmbhatt, MD, Chaya Shwaartz, MD, Andreas Prachalias, MD, Parthi Srinivasan, MBBS, FRCS, FRCS, Wayel Jassem, PhD, FRCS, Nigel Heaton, FRCS, Mark S. Cattral, MD, MSc, Nazia Selzner, MD, PhD, Anand Ghanekar, MD, PhD, Gabriela Morgenshtern, Neil Mehta, MD, Allan B. Massie, PhD, MHS, Jan van der Meulen, PhD, Dorry L. Segev, MD, PhD, and Gonzalo Sapisochin, MD, PhD, MSc (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.035). It appears online in advance of the Journal of Hepatology, volume 77, issue 5 (November 2022) published by Elsevier.
Full text of this article is available to credentialed journalists upon request; contact Freya Weise at +33 6 28 51 59 51 or hmsmedia@elsevier.com. Journalists wishing to interview the authors should contact Dr. Gonzalo Sapisochin at Gonzalo.sapisochin@uhn.ca, or Ana Fernandes, Senior Public Affairs Advisor, University Health Network, at +1 437 216 4597 or ana.fernandes@uhn.ca.
About the Journal of Hepatology
The Journal of Hepatology, the premier journal devoted to liver diseases, is the official journal of the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL). It publishes original papers, reviews, case reports, and letters to the Editor concerned with clinical and basic research in the field of hepatology. The journal has a 2021 Impact Factor of 30.083 (Source: Journal Citation Reports™ from Clarivate, 2022). www.journal-of-hepatology.eu
About EASL
In the fifty plus years since EASL was founded, it has grown from a small organization that played host to 70 participants at its first meeting, to becoming the leading international liver association. EASL attracts the foremost hepatology experts as members and has an impressive track record in promoting research in liver disease, supporting wider education, and promoting changes in European liver policy. www.easl.eu
About Elsevier
As a global leader in information and analytics, Elsevier helps researchers and healthcare professionals advance science and improve health outcomes for the benefit of society. We do this by facilitating insights and critical decision-making for customers across the global research and health ecosystems.
In everything we publish, we uphold the highest standards of quality and integrity. We bring that same rigor to our information analytics solutions for researchers, health professionals, institutions and funders.
Elsevier employs 8,700 people worldwide. We have supported the work of our research and health partners for more than 140 years. Growing from our roots in publishing, we offer knowledge and valuable analytics that help our users make breakthroughs and drive societal progress. Digital solutions such as ScienceDirect, Scopus, SciVal, ClinicalKey and Sherpath support strategic research management, R&D performance, clinical decision support, and health education. Researchers and healthcare professionals rely on our over 2,700 digitized journals, including The Lancet and Cell; our over 43,000 eBook titles; and our iconic reference works, such as Gray’s Anatomy. With the Elsevier Foundation and our external Inclusion & Diversity Advisory Board, we work in partnership with diverse stakeholders to advance inclusion and diversity in science, research and healthcare in developing countries and around the world.
Elsevier is part of RELX, a global provider of information-based analytics and decision tools for professional and business customers. www.elsevier.com

